What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
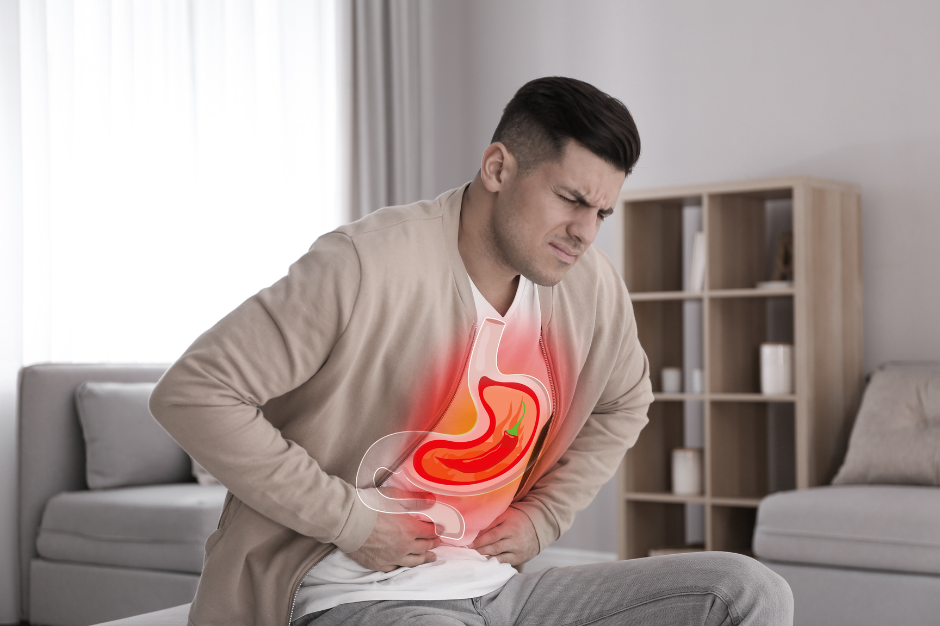
IBS is a chronic disorder of the digestive system, characterized by a range of symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation. These symptoms can vary in severity and duration, often disrupting daily life and impacting emotional well-being. IBS can significantly affect quality of life and mental health.
Symptoms of IBS
Understanding the symptoms of IBS is key to recognizing and managing the condition. Some common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort: This may vary in intensity and may be relieved by a bowel movement.
- Bloating and gas: Excessive gas production and bloating are common complaints among individuals with IBS.
- Altered bowel habits: Some people may experience diarrhea, while others may have constipation. Some individuals may alternate between the two.
- Changes in stool consistency: Stools may vary in consistency, appearing loose or hard, and may contain mucus.
- Urgency: A sudden and urgent need to have a bowel movement is another common symptom.
Triggers of IBS
Identifying triggers is essential for managing IBS symptoms. While triggers can vary from person to person, some common ones include:
- Dietary factors: Certain foods and beverages, such as spicy foods, dairy products, caffeine, and alcohol, can trigger symptoms.
- Stress and anxiety: Emotional stress and anxiety can exacerbate IBS symptoms or trigger flare-ups.
- Hormonal changes: For some individuals, hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during menstruation, can affect IBS symptoms.
- Medications: Some medications, including certain antibiotics and pain relievers, can worsen symptoms in some individuals.
- Gut microbiota imbalance: Disruptions in the balance of bacteria in the gut may contribute to IBS symptoms in some cases.
Managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Several management strategies can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Dietary modifications: Keeping a food diary can help identify trigger foods, allowing individuals to make informed dietary choices. Some may benefit from following a low-FODMAP diet or eliminating specific trigger foods.
- Stress management: Techniques such as relaxation exercises, meditation, and mindfulness can help reduce stress and alleviate IBS symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, adequate sleep, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall well-being and symptom management.
- Therapy: Herbal medicine, acupuncture, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), hypnotherapy, or counseling may be beneficial for addressing underlying physical and psychological factors contributing to IBS symptoms.
The Importance of Open Dialogue
Despite its prevalence, IBS is often accompanied by feelings of embarrassment, shame, and isolation. Many individuals struggle to discuss their symptoms openly due to societal taboos surrounding digestive health.
If you need help
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a complex and often challenging condition. At Happipuncture, we can create a more supportive and understanding environment for those living with the condition. Let’s keep the conversation going and work together to increase the quality of your life. Contact us for a free initial consultation at Happipuncture or call 09-2182992.