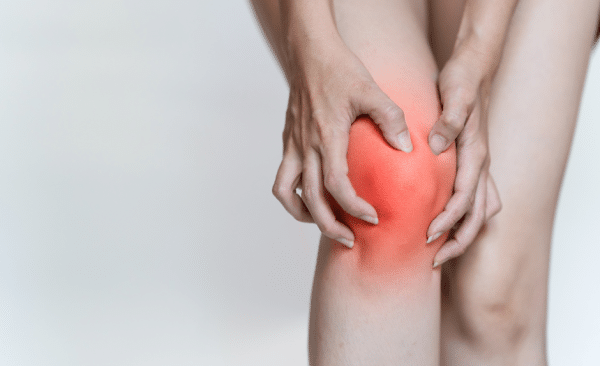
Arthritis
What is Arthritis?
Causes of Arthritis
- Genetics: Some types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), have a genetic component, meaning they can run in families. Individuals with a family history of arthritis may have a higher risk of developing the condition.
- Age: Osteoarthritis (OA), the most common type of arthritis, is often associated with aging. As people get older, the cartilage that cushions the joints may wear down over time, leading to joint pain and stiffness.
- Joint Injury: Trauma or injury to a joint can increase the risk of developing arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis. Activities that involve repetitive stress on the joints, such as sports or heavy lifting, can also contribute to joint damage and arthritis.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other autoimmune conditions occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing inflammation and damage. Autoimmune disorders can have genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors that contribute to their development.
- Obesity: Excess body weight puts additional stress on the joints, particularly the knees, hips, and spine. Obesity is a significant risk factor for osteoarthritis, as it accelerates joint degeneration and increases inflammation in the body.
- Infection: In some cases, arthritis can develop as a result of an infection in the joint, known as septic arthritis. Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can trigger inflammation and damage to the joint tissues.
- Metabolic Disorders: Metabolic conditions such as gout and pseudogout can cause arthritis-like symptoms due to the buildup of uric acid crystals or calcium crystals in the joints, leading to inflammation and pain.
What self-care Method Can Help Arthritis?
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling can help improve joint flexibility, strengthen muscles around the joints, and reduce pain. Range-of-motion exercises and gentle stretching can also help maintain joint mobility.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing arthritis, especially osteoarthritis. Excess body weight puts additional stress on the joints, leading to increased pain and inflammation. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can support weight management and promote joint health.
- Hot and Cold Therapy: Applying heat packs or warm compresses to sore joints can help relax muscles, reduce stiffness, and alleviate pain. Cold therapy, such as ice packs or cold compresses, can help reduce inflammation and numb pain in swollen joints. Alternating between hot and cold treatments can provide relief for arthritis symptoms.
- Joint Protection: Avoid activities that exacerbate joint pain or strain, and use assistive devices such as braces, splints, or walking aids to support and protect affected joints. Ergonomic modifications to the home and workplace can also help reduce joint stress and improve overall comfort.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can exacerbate arthritis symptoms by triggering inflammation and worsening pain. Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or tai chi can help promote relaxation, reduce muscle tension, and improve overall well-being.
- Healthy Sleep Habits: Prioritize getting adequate sleep each night to support overall health and pain management. Establish a regular sleep schedule, create a comfortable sleep environment, and practice relaxation techniques before bedtime to improve sleep quality.
- Dietary Modifications: Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods such as fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and colorful fruits and vegetables into your diet to help reduce inflammation and support joint health. Limiting processed foods, sugary beverages, and foods high in saturated fats can also help manage arthritis symptoms.
How Can We Help?